Fail2ban help our servers to prevent the brute force attacks scanning the log files to find fail authentication attempts. Software like hydra http://www.thc.org/thc-hydra/ can attempt to login in service that require authentication like telnet, ssh, http, ftp, etc… trying with an user and password combination based in dictionary. If our password have a strong combination It’s very difficult to obtain the access with this method, but the attempts will generate unnecessary traffic.
With Fail2ban there are some terms to define for config files:
- filter: is a regular expression with must match a pattern corresponding with a failure in log file.
- action: Define various commands executed in different moments.
- jail: a combination of one filter and action.
In this scenario I’ll configure Fail2ban with a SSH server filtering with iptables and a FTP server (vsftpd) filtered by TCP wrappers using the file /etc/hosts.deny.
1.- Install EPEL repository from:
# rpm -ivh http://ftp.cica.es/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-7.noarch.rpm
2.- Install Fail2Ban and postfix to mail notifications:
# yum install fail2ban postfix mailx
3.- Edit the main config file /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf:
[DEFAULT]
# Fail2ban will not ban a host which matches an address in this list ignoreip = 127.0.0.1 # "bantime" is the number of seconds that a host is banned. bantime = 600 # A host is banned if it has generated "maxretry" during the last "findtime". findtime = 600 # "maxretry" is the number of failures before a host get banned. maxretry = 3 # "backend" specifies the backend used to get files modification. backend = auto
[ssh-iptables]
enabled = true filter = sshd action = iptables[name=SSH, port=ssh, protocol=tcp] sendmail-whois[name=SSH, dest=root, [email protected]] logpath = /var/log/secure maxretry = 5
[vsftpd-tcpwrapper]
enabled = true filter = vsftpd action = hostsdeny[file=/etc/hosts.deny] sendmail-whois[name=VSFTPD, dest=root, [email protected]] logpath = /var/log/vsftpd.log maxretry = 5 bantime = 1800
4.- Start the services:
# service postfix start # chkconfig --levels 235 postfix on # service fail2ban start # chkconfig --levels 235 fail2ban on
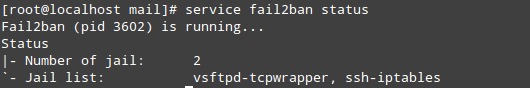
5.- Test the jail configured:
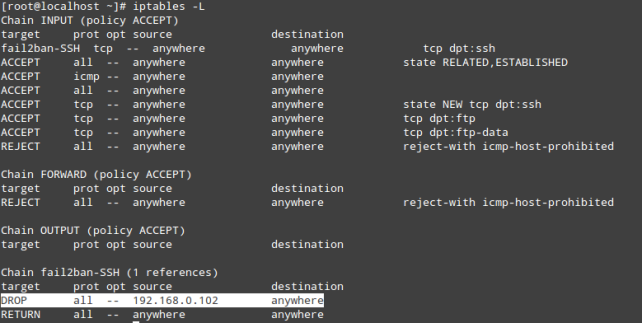
- See the iptables rules generated by Fail2ban after a brute force attack to SSH service:
- To unban an IP address banned by iptables run this:
# iptables -D fail2ban-SSH -s 192.168.0.102 -j DROP
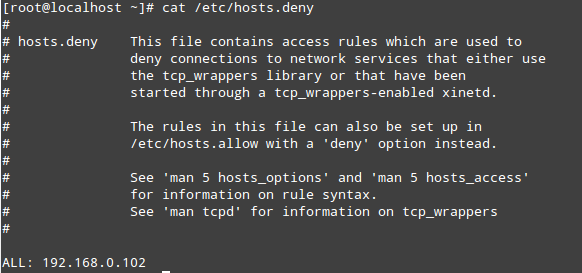
- See the file /etc/hosts.deny after brute force attack in FTP server:
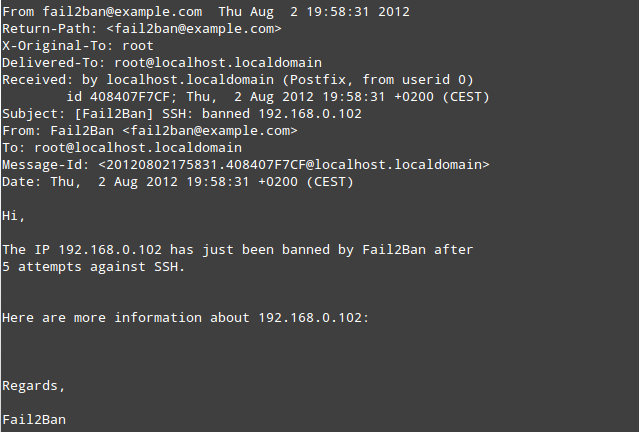
- Mail notification from SSH attack:
Official page of Fail2ban project:
http://www.fail2ban.org/wiki/index.php/Main_Page